In this paper, results are presented of propagation experiments conducted to verify the accuracy of a novel ray-optical scattering model for EES.
Scalable Modeling of Human Blockage at Millimeter-Wave: A Comparative Analysis of Knife-Edge Diffraction, the Uniform Theory of Diffraction, and Physical Optics Against 60 GHz Channel Measurements
Human blockage at millimeter-wave frequencies is most commonly modeled through Knife-Edge Diffraction (KED) from the edges of the body shaped as a vertical strip. Although extensively validated in controlled laboratory experiments, the model does not scale to realistic 3D scenarios with many, randomly oriented bodies, on which multipath signals can be incident from any direction, not just normal to the strip. To address this, in this article we investigate computational electromagnetic methods based on raytracing.
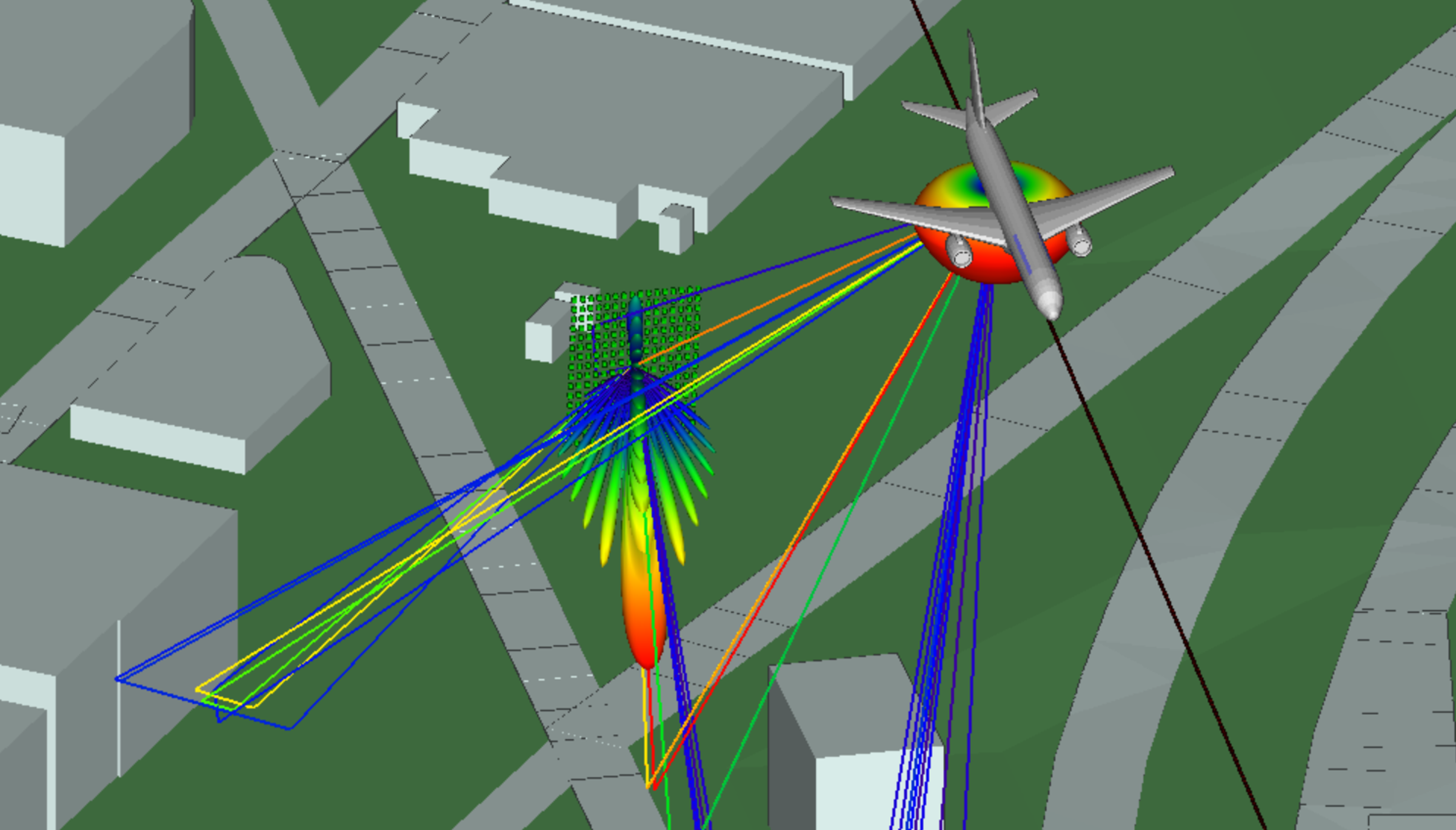
Assessing 5G Radar Altimeter Interference for Realistic Instrument Landing System Approaches
The safe rollout of new or enhanced 5G services using C-band spectrum near airports in 2022-2023 will require realistic modeling of radio propagation to mitigate potential interference with legacy radar altimeters which remain in operation as of summer 2022. In this whitepaper, we use Wireless InSite to provide a realistic assessment of radar altimeter interference due to emissions from 5G base stations along a landing approach to runway 27L of Chicago O’Hare International Airport.
5G Millimeter Wave Frequencies and Mobile Networks Technology Whitepaper
Using EM Simulation for 5G Design E-Book
Simulating Throughput as a Device Design Metric
Simulation of Beamforming by Massive MIMO Antennas in Dense Urban Environments
This presentation demonstrates a predictive capability for simulating massive MIMO antennas and beamforming in dense urban propagation environments. Remcom's unique approach allows us to predict the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) at specific device locations and the actual physical beams formed using these techniques, including unintentional distortions caused by pilot contamination.
Wireless InSite Simulation of MIMO Antennas for 5G Telecommunications
To keep up with rising demand and new technologies, the wireless industry is researching a wide array of solutions for 5G, including Massive MIMO. Remcom’s Wireless InSite provides an efficient method to predict channel characteristics for large-array MIMO antennas in complex multipath environments.
Comparison of Indoor Propagation Modeling of WiFi Coverage Using Wireless InSite and Measurements
This presentation demonstrates how the 3D ray tracing code in Wireless InSite can accurately predict received power coverage even in a multi-room environment containing many walls and different materials types. In order to verify the accuracy of the code, the floor plan of Remcom’s business offices was modeled in the software with a WiFi antenna and a third party tool was used to create a coverage plot of the received power throughout several of the suites.
Empirical / Ray-tracing Hybrid Approach for COST 231 Unknown Building Layouts
Uncertainty in structure geometry is a fundamental limitation of ray-tracing methods when simulating urban propagation. We present a hybrid approach using ray-tracing methods and empirically derived loss factors to incorporate the effect of unknown interior layouts. This approach is compared with a more typical empirical implementation to demonstrate the benefits of hybridization.
High Fidelity Modeling of Spatio-Temporally Dense Multi-Radio Scenarios
Heterogeneous, mobile wireless networks are becoming increasingly difficult to validate for operational use. Presented is an approach to reduce the run-time of these high fidelity simulations by constructing precise results based on adjacent ray-paths from a lower resolution simulation. Speed and accuracy trade-offs are presented for this approach in typical urban scenarios, demonstrating its effectiveness in meeting the growing needs of wireless channel emulation.
Modeling RF Attenuation in a Mine Due to Tunnel Diameter and Shape
Accurately characterizing the propagation of RF signals in tunnels is important for rescue, safety, and military purposes. The material composition of the tunnel, the tunnel shape and size, obstructions, and tunnel bends present challenges. In this paper we use Wireless InSite to analyze how tunnel diameter and shape affect the propagation characteristics.
Modeling RF Propagation in Mines Using Wireless InSite
Complex 3D Modeling of Sea to Land Scenario
This paper presents results from sea to land propagation using Wireless InSite. The effort explores the effects of various elements in the scene and how they impact the results. The various elements in the scene include the ships out at sea, the ships docked, the docks themselves, the buildings around the dock area, and the material properties of each.
CUDA Implementation of Moving Window Finite-Difference Time-Domain
Indoor Channel Measurement and Prediction for 802.11n System
Significant improvements in the quality and reliability of indoor WLAN communications are claimed for devices with MIMO technology applying 802.11n standards, which allow users to achieve a theoretical data rate up to 300-600 Mbps on a single transmission. This paper presents an analysis of a commercial 802.11n MIMO 2×3 dual band (2.4 and 5 GHz) system focusing on the operational throughput performance over an indoor environment for Line of Sight (LOS) and Non Line of Sight (NLOS) scenarios.